Introduction
Although the topic of laundry in the Netherlands may seem odd to begin a talk on sustainable eating and reducing food waste, it serves as a reminder that sustainability applies to many different facets of our lives. We should attempt to limit food waste in our homes, just as we try to use as little energy and water as possible while doing laundry. Food waste is a major problem that has negative effects on the environment, the economy, and society.
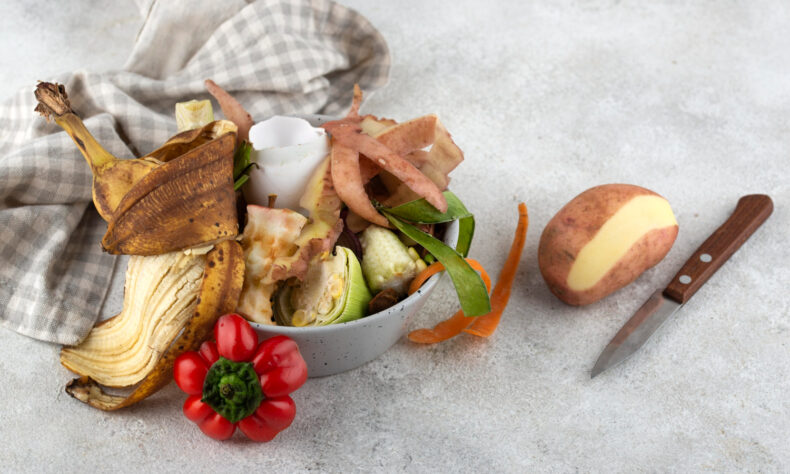
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations estimates that every year, some 1.3 billion tons of food intended for human use are lost or wasted. This waste puts a burden on our natural resources, increases food poverty, and adds to greenhouse gas emissions.
In this blog, we’ll discuss the significance of eating sustainably and provide helpful advice on how to cut down on food waste at home, ensuring that we not only save money but also help the environment.
The Impact of Food Waste
Understanding the extent of the issue and the implications it bears is crucial before going into options for decreasing food waste. Food waste has an impact on many facets of our society, and finding solutions is essential for a sustainable future.
Environmental Impact: When food waste breaks down in landfills, it releases a considerable amount of greenhouse gases, mostly methane. Reduced organic waste entering these locations is crucial since these emissions contribute to climate change.
Resource Depletion: Large quantities of resources, including water, land, and energy, are needed to produce food. We waste these important resources when we throw away food. Keeping these inputs under check and ensuring more sustainable use of our planet’s limited resources are both achieved through reducing food waste.
Economic Costs: Financial hardship is caused by food waste for individuals, organizations, and governments. Reducing food waste may result in significant financial savings for an individual. It may increase corporate profitability and lower government spending on trash management and disposal.
Food Security: Improving global food security may be significantly aided by reducing food waste. Consumer waste may be reduced, which will free up more food to feed the expanding world population.
After discussing the need to decrease food waste, let’s examine some doable methods for establishing sustainable eating practices at home.
Tips for Reducing Food Waste at Home
Plan Your Meals: Planning your meals is one of the best methods to reduce food waste. Make a list of the ingredients you’ll need for the week’s worth of meals before you go shopping. Keep to your list and abstain from impulsive purchases. By buying just what you’ll need, you may lessen the chance that food will deteriorate before you can eat it.
Practice First-In, First-Out (FIFO): When unloading groceries, put the most recent things towards the rear of the pantry or refrigerator and the older ones in the front. By doing this, you may save food waste by using older components before they expire.
Understand Expiry Dates: Expiry dates can be confusing, with terms like “use by,” “sell by,” and “best before.” Familiarize yourself with these labels and their meanings. Often, food items are still safe to consume after the “best before” date, but you should exercise caution with items labeled “use by.”
Proper Storage: Properly storing food can extend its shelf life. For example, store fruits and vegetables in the crisper drawer of your refrigerator, keep bread in a cool, dry place, and use airtight containers for leftovers. Understanding the optimal storage conditions for different foods is essential.
Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes when cooking and serving meals. Prepare only what you can eat, and consider reducing recipes if they make more food than your household can consume. Leftovers can be a significant source of food waste.
Get Creative with Leftovers: Instead of tossing leftovers, get creative with how you can repurpose them into new dishes. For example, last night’s roasted vegetables can become a delicious frittata or pizza topping, and overripe bananas are perfect for baking banana bread.
Freeze Excess Food: If you find yourself with surplus food that you can’t consume in time, freeze it. Many items, including meat, bread, and fruits, can be frozen to extend their shelf life. Just be sure to label and date items to keep track of what’s in your freezer.
Composting: Unavoidable food waste includes peels, cores, and crumbs. Start a composting system as an alternative to disposing of them. Your garden soil may be improved by compost, eliminating the requirement for chemical fertilizers.
Donate Unwanted Food: Consider giving non-perishable food goods to a nearby food bank or charity if you have any that you won’t need. To aid individuals in need, several organizations welcome gifts of unopened, non-expired food.
Educate Yourself: Understand how to reduce food waste and how your food choices affect the environment. You’ll be better able to make sustainable selections the more you know.
Cultural and Global Considerations
It takes a worldwide effort to reduce food waste, one that includes companies, communities, and government agencies. Several cultural and international factors to bear in mind are listed below:
Cultural Awareness: Different cultures have varying attitudes toward food and waste. It’s important to be sensitive to cultural differences while promoting food waste reduction.
Government Initiatives: Numerous countries are taking action to decrease food waste, from enacting laws governing food labeling to assisting food rescue initiatives. Keep up with these activities and, if you can, provide your support.
Business Practices: Reducing food waste is a major responsibility of the food business. Support eateries and grocery businesses that place a high priority on sustainability and minimize food waste.
Community Engagement: Participate in regional initiatives to reduce food waste, such as neighborhood composting programs or food recovery groups. At the local level, these measures may have a significant influence.
Conclusion
Even though it may not seem that laundry in the Netherlands has anything to do with eating sustainably, both ideas have one thing in common: the desire to live sustainably. Food waste is a major problem that has negative effects on the economy, the environment, and food security. We can all help to lessen food waste and the issues it causes by establishing sustainable eating habits at home, such as meal planning, appropriate storage, and composting.
Keep in mind that decreasing food waste involves the efforts of many people, including those in communities, corporations, and governments. We can make considerable progress toward a more sustainable and secure food future for everybody by increasing awareness, supporting regional efforts, and making thoughtful decisions. Therefore, let’s all work together to reduce food waste and improve the earth, one meal at a time.